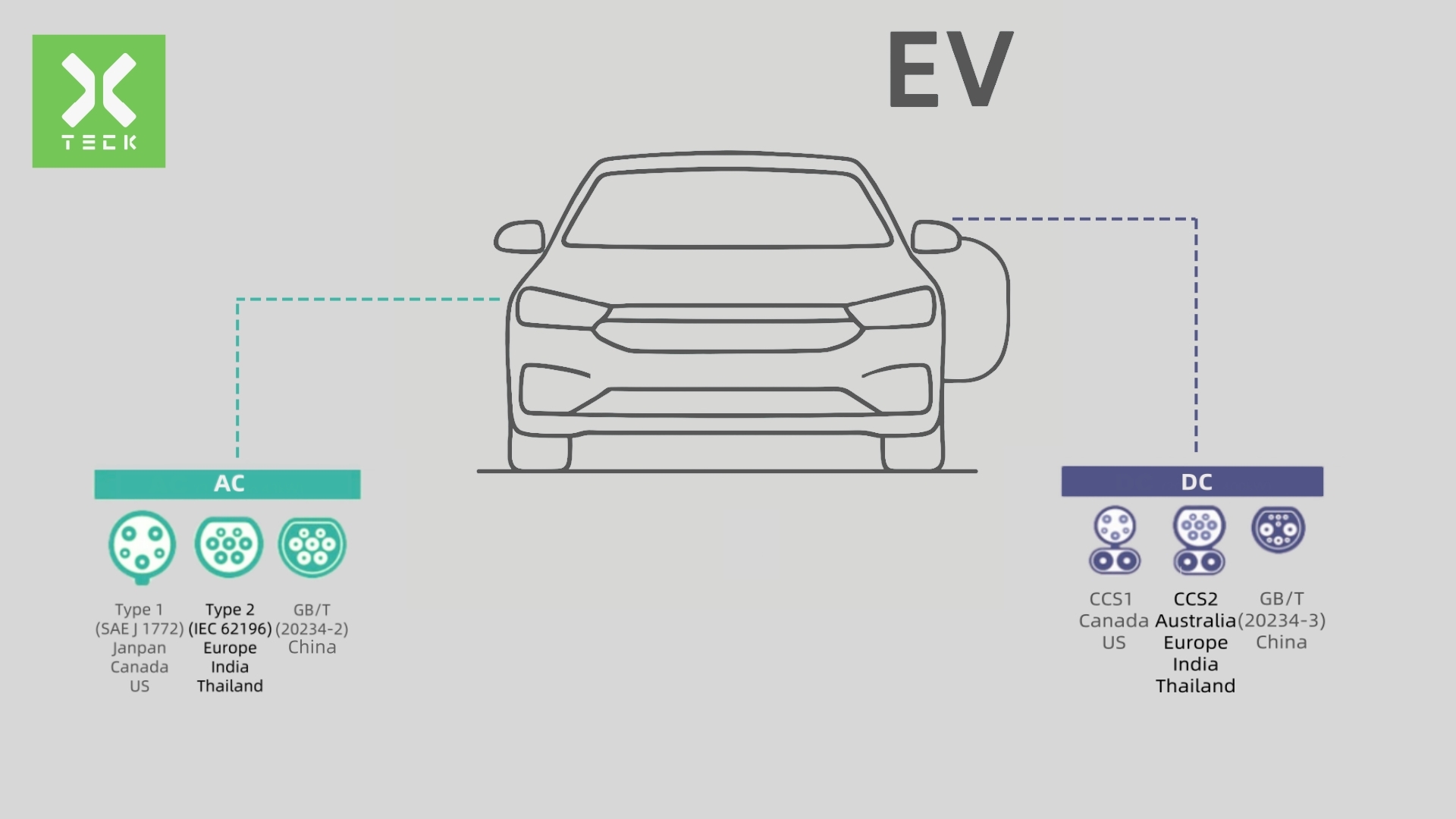
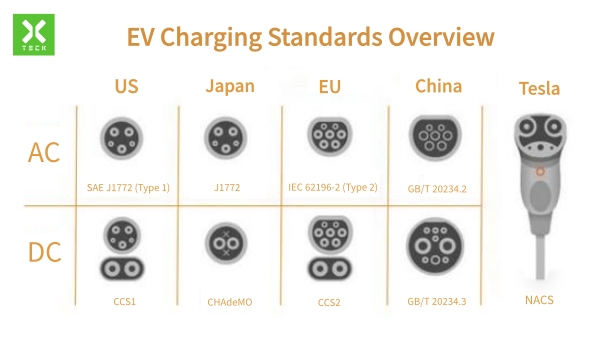
-
Products
- Type 1 to Type 2
- Type 2 to Type 2
- Type 1 Tethered Cable
- Type 2 Tethered Cable
- Tesla Charging Cable
- Read More
- Type 1 to Type 2
- Type 2 to Type 2
- Type 2 to Type 1
- Type 2 to GBT
- Tesla to J1772
- Read More
- 60kW 90kW 120kW DC Charger Pile Advertising Screen Floor Mounted EV Charging Station
- GBT CCS1 CCS2 NACS CHAdeMO EV DC Charging Station 60kW-120 kW With OCPP1.6J
- 60kW 90kW 120kW DC Charging Station OCPP1.6 Floor Mounted Advertising EV Charging Station 55 inch screen
- 40kW-240kW Fast DC EV Charger with 2 CCS1 CCS2 CHAdeMO NACS GB/T Cables
- OCPP DC Fast EV Charger 60-240kW Commercial CHAdeMO CCS2 Dual Port Smart Ev Charging Station
- Customized 60kW 90kW 120kW 160kW 180kW 240kW Dual Gun CCS2 CHAdeMo GB/T Fast Charging Station
- 60kW 80kW 120kW 160kW 180kW 240kW CCS1 CCS2 GBT CHAdeMo DC EV Charging Station
- DC Portable Charger 20KW Ccs2 Fast Mobile Charging Station
- DC Fast EV Charger GB/T 20kW Portable EV Charging Station
- 20kW 30kW Ccs2 GBT Portable DC EV Charger manufacturers & Suppliers
- 7kW 15kW 20kW 30kW 40kW CCS1 CCS2 GBT CHAdeMo Portable DC EV Charger
- 20kW 30kW 40kW CCS2 CCS1 Chademo GBT Portable DC Fast EV Charger
- 7kw 15kW 20kW 30kW 40kW 50kW 60kW CCS2 CCS1 Chademo GBT Portable DC Fast EV Charger
- 7kw 15kw 20kw 30kw 40kw Chademo GBT CCS1 CCS2 Portable DC EV Fast Charger
- EV Mobile Charging Station 65kWh 60kW Rescue Car Energy Storage Charging System
- 65kWh Mobile EV Charger 60kW Portable Battery-Powered Fast Charging Station
- EV Charging Station 141kWh 120 EV Battery Fast Charging Rescue Car Energy Storage Charging System
- Road Rescue DC Fast Portable Charging 141kWh 120kW Mobile Station with Battery
- 141kwh 161kwh Battery Charging Station 120kw Charging Station for Road Assistance
- 161KWh 120KW Portable Electric Car Energy Storage Charging Station for Road Emergency Rescue
- 14kW 22kW 44kW Dual Plug Floor-Mounted AC EV Charger for Commercial Use
- 14kW 22kW 44kW Floor-Mounted Dual Gun EV AC Charger for Business
- Commercial Floor-Mounted Dual Gun AC EV Charger 14kW 22kW 44kW
- High Efficiency 14kW 22kW 44kW Dual Gun Floor AC EV Charging Station
- 44KW AC EV Charger - Fast Charging for Electric Vehicles
- 14kW 22kW 44kw AC Charging Station with Dual Cable IEC 62196-2 Type2 EV Charger
- Commercial Ues 14kW 22kW 44kW Floor Standing AC EV Charger With Dual Gun
- 44KW Wallbox 2 x 22kW EV Charging Station with Dual Type 2 Socket AC Public Charging Station
- 14kW 22kW 44kW Commercial Double Gun AC Floor Mounted Charging Station
- 44kW Commercial AC EV Charger With Advertising Screen
- Evse Home Wallbox Level 2 Fast Charging Station 7kw 11KW 22KW 16A 32A Type 2 Type 1 EV Charger With Screen
- Smart Home Eves Walbox 7kw 1lKW 22KW Type2 AC Charging Station With Ocpp1.6 Wifi App
- 32A 22KW 3Phase EVSE Wallbox IEC62196 Type2 Electric Vehicle Car Charger with RFID Card APP EV Home
- Home 7kW 11kW 22kW Wallbox Type2 1Phase 3 Phase 16A 32A RFID APP 22KW EV Charger
- Eletric Car Charging Station 7kW 11kW 22kW Wallbox Type2 AC Charging Station
- Type 2 Socket IEC 62196-2 22KW For Electric Vehicle EV Charger 32A 3 Phase EVSE Wallbox EV Charging Station
- 14kW 22kW 44kW Commercial Double Gun AC Wall Charging Station
- 7kw 11kw 22kw 16A 32A Mode 3 OCPP APP WIFI Wallbox EV Charger
- 32A 7kW Portable Ev charger Type 2 Ev charging Cable Type A Dc 6mA IP65 Electric Vehicle charger
- 16A 20A 24A 32Amp Type 2 Portable EV Charger 7kW home charger EV Charger Box
- 7kW EV Charger Single Phase Level 2 Type 2 Charger for Electric Car
- 7KW Level 2 EV Charger Portable EVSE Electric car charger With NACs Plug For Tesla
- 16Amp 3.5KW 240V Mobile Charger Tesla Home Charger for ModelY/3/S/X
- 7kW Level2 Portable Ev charger 40A Adjustable Current Tesla Portable Electric vehicle charger
- 16A 3.5kW Mode 2 Home charger Type 2 EV Portable Vehicle charger
- 16A 32A EV Portable charger Type 2 Level 2 Home charger
- Type 2 Mobile Ev car charger 32A 7kW Home Charger CEE Plug
- 7kW 11kw 22kw 32a 16a Home Type2 Portable EV Fast Charger
- Portable EV Charger Type 2 time delay 16A 32A EU Plug IEC62196-2 EV Charging Cable
- 32A 3 phase Portable EV Charger for 400V EV Charging Type2 with Red CEE
- 3 Phase AC Charging 22kw 32A Type 2 EV Charger EVSE Wallbox
- 3 Phase 11KW 16Amp IEC 62169 Type 2 EV Charger Modes 2 EV Charging with 5 Pin Red CEE Plug
- Portable EV Charging Station IEC 62196-2 Type 2 Plug 8A 10A 16A Level 2 EV Charger
- New Design 32A 7.4KW Type 2 EVSE Controller with Blue Cee
- Portable EV Charger Type 1 16A 32A level 2 EV Charger Electric Vehicle Charging Cable for Tesla Model Y
- Mode 2 EV Charger Type 2 7kw 16A 32A IP67 Time Delay Portable Type 2 Charging Cable
- 32A Adjustable EV Charger J1772 Plug EVSE Type 1 EV Charging Cable Electric Vehicle Charging box
- 32A 40Amp EV Charger Level 2 Type 1 J1772 Plug NEMA 14-50 Portable Electric Vehicle Charging Station
- J1772 Type 1 EV Charging Cable 3 Pin 8A 10A 13A IP67 Portable EV Charger
- IEC 62196 Type 2 Female EV Charging Socket 1/3phase 16A/32A Type 2 EV Socket
- IEC 62196-2 EV Charger 32Amp 3 Phase Type 2 Female EV Connector Socket for Wallbox
- Type2 EVSE IEC 62196-2 Connector Socket Plug Mount AC Dummy Station
- 16A 32A IEC 62196 Type 2 EV Charger Socket With Shutter
- 16A 32A 3 Phase IEC62196-2 Type 2 Outlet Sockets with Solenoid Lock and Shutter

- Solutions
- Resources
-
OEM EV Charger
-
Services
- About Us
- Blog